Configuring Autotask integration with Dark Web ID
This guide provides step‑by‑step instructions for enabling the Dark Web ID integration with Autotask. When enabled, Dark Web ID automatically creates an Autotask ticket for each newly discovered compromise, allowing you to triage, track, and remediate security incidents directly from Autotask.
Integration overview
The Autotask integration enhances Dark Web ID by automatically creating a PSA service ticket for each new compromise detected. This improves visibility, reduces response time, and centralizes incident management within Autotask.
NOTE The integration is one‑way. Dark Web ID sends compromise data to Autotask but does not receive ticket updates or status changes.
Prerequisites
Before configuring the integration, ensure that:
-
You have access to both Dark Web ID and Autotask PSA
-
You have administrative permissions in Autotask to create an API user
-
You can identify or create an Autotask company that maps to a Dark Web ID organization
IMPORTANT Complete the sections in this article in the order presented. Later configuration steps depend on permissions, roles, and API objects created in earlier sections.
How to...
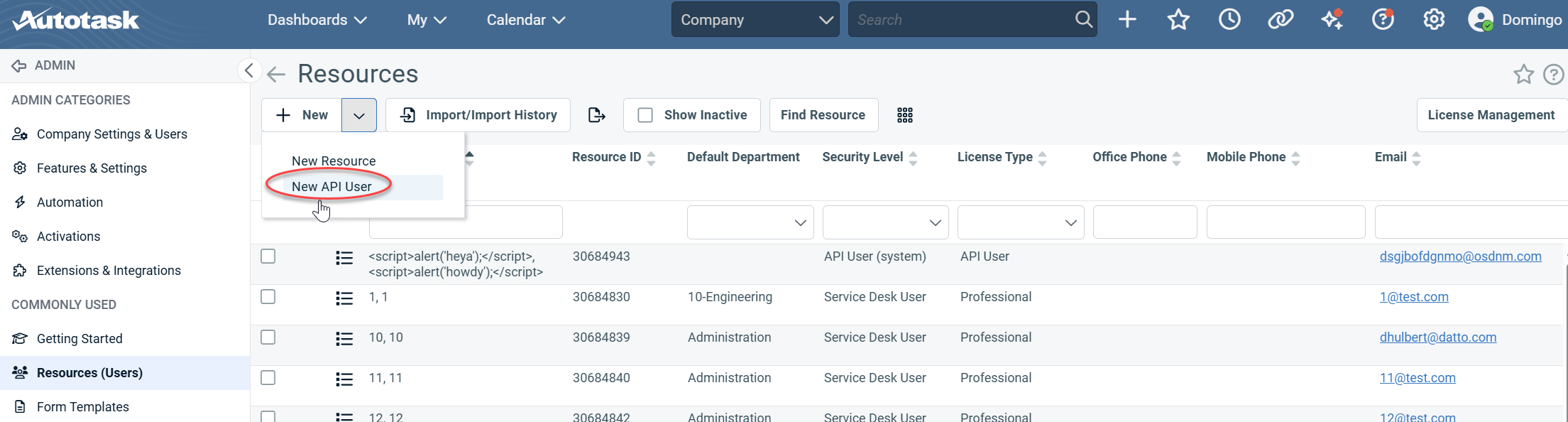
1. From the Autotask dashboard, click Admin in the side navigation menu.
2. Click Resources (Users).
3. Select New API User from the + New drop-down menu.
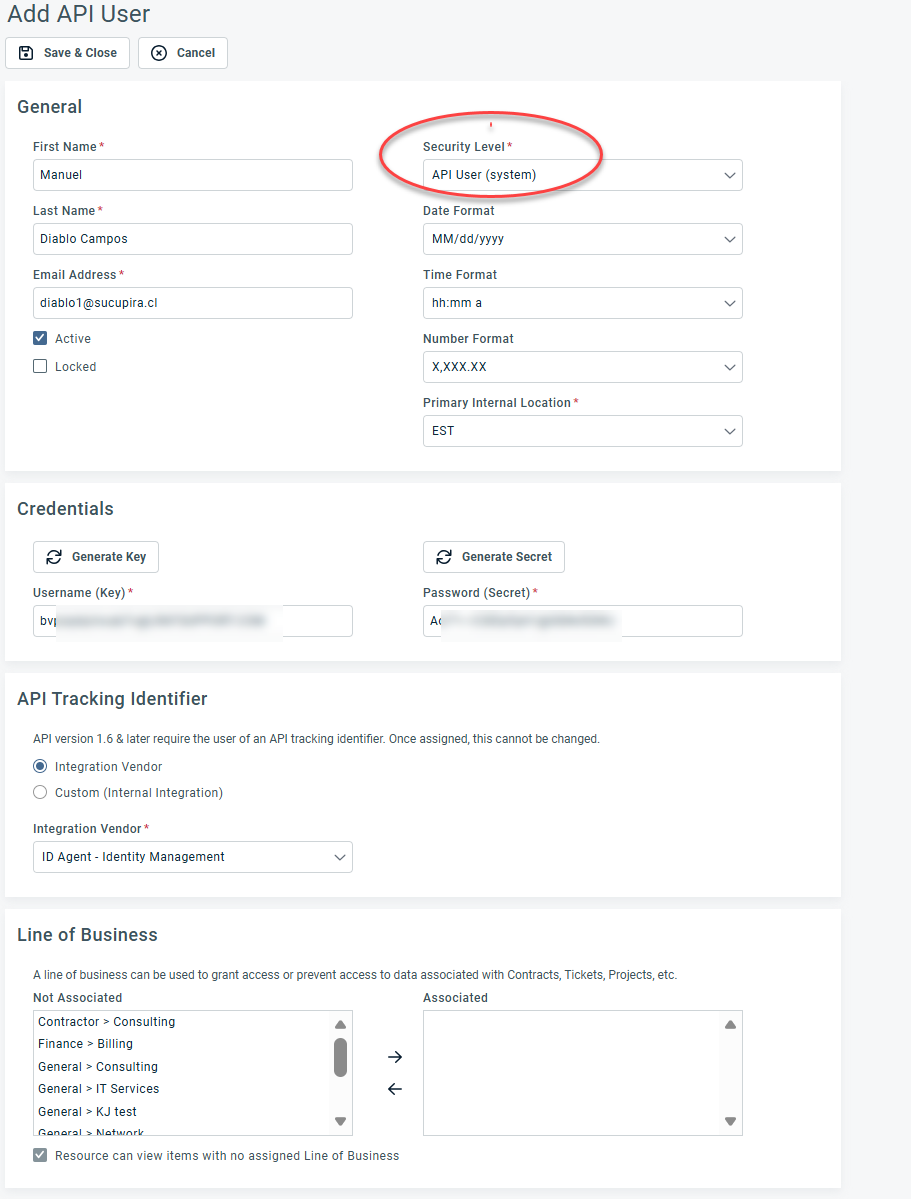
4. Complete the required fields and ensure the Security Level is set to API User.
5. Click Generate Key and Generate Secret.
IMPORTANT Copy both the key and secret. You will need them when configuring the integration in Dark Web ID.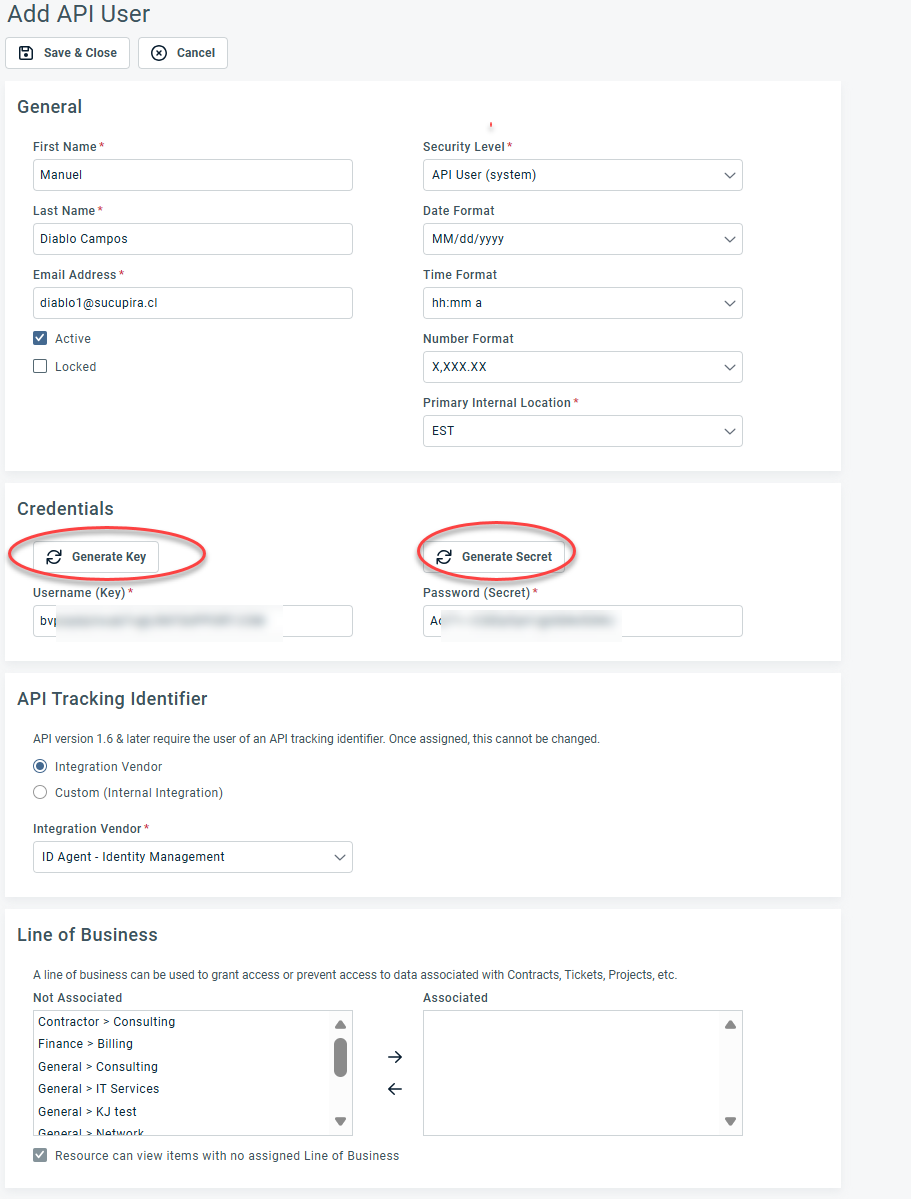
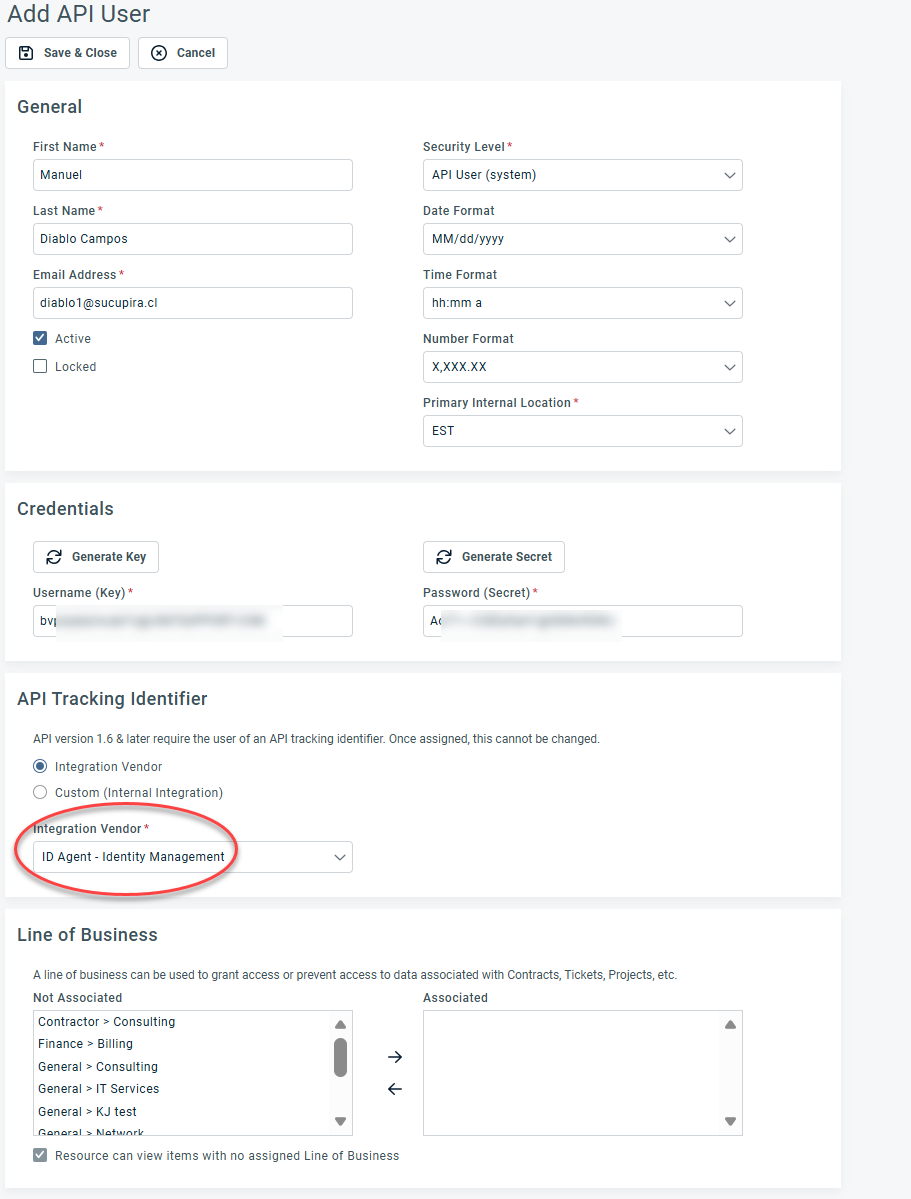
6. In the API Tracking Identifier section, select ID Agent - Identity Management in the Integration Vendor drop-down menu.
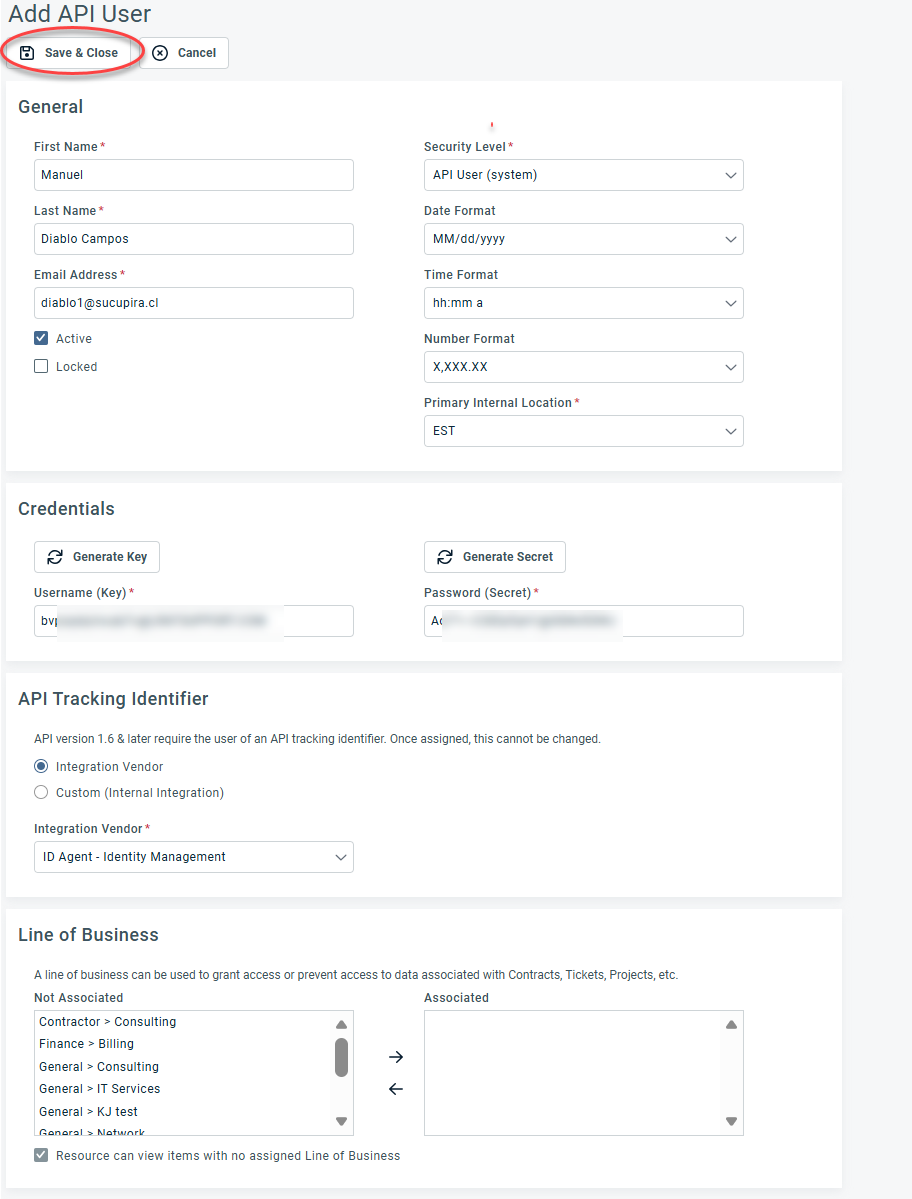
7. Click Save & Close. This will add a new API user to the application.
1. Log in to Dark Web ID.
2. From the side navigation menu, click Integrations.
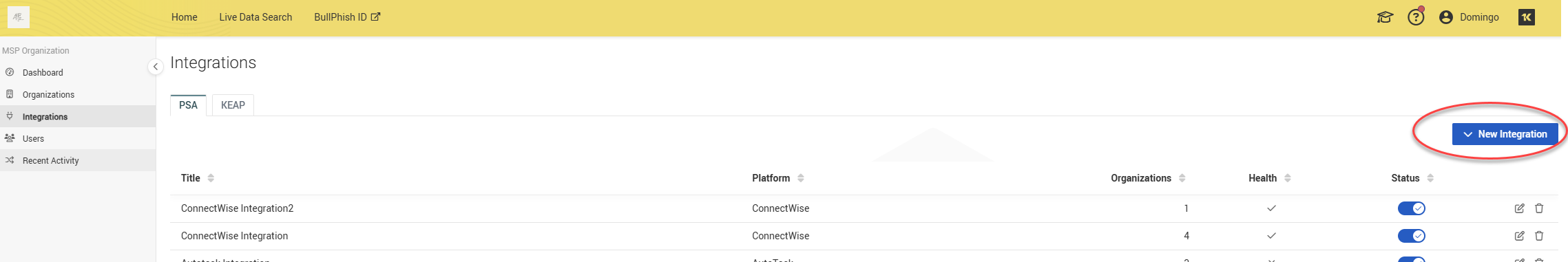
3. Under the PSA tab, click New integration.
4. Select Autotask from the New Integration drop-down menu.
5. On the Create Integration page, enter a name for the integration.
NOTE You can create multiple Autotask integrations. Use clear names to distinguish them.
-
Enter the following required information under Credentials:
Field Description Autotask API version Enter your Autotask API version. It is recommended to use version 1.6. Autotask Username Enter theUsername (Key) generated in Create an API user in Autotask. Autotask Password Enter the Password (Secret) generated in Create an API user in Autotask. -
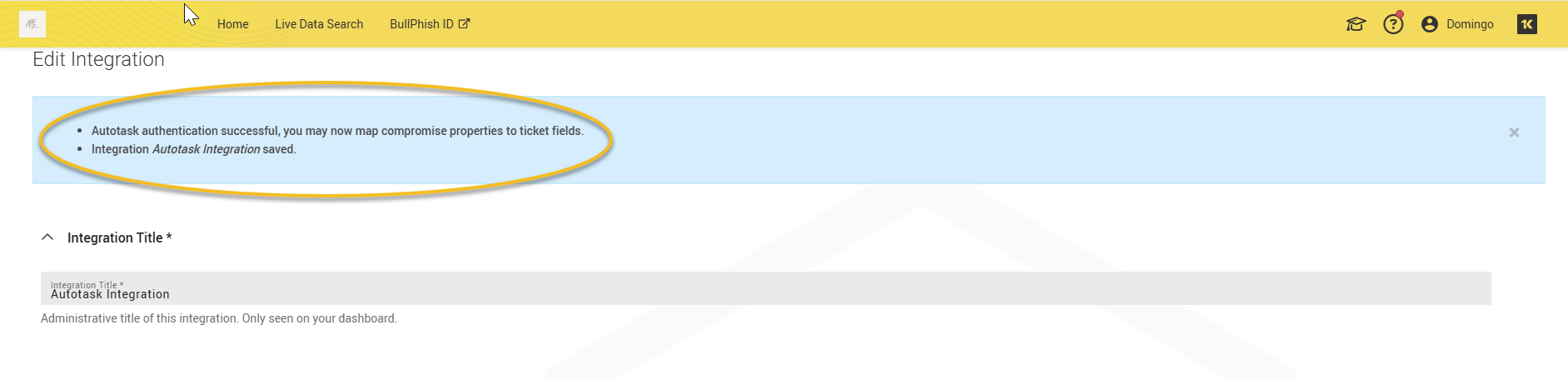
Click Save. A success message confirms authentication.
Under Ticket Conditions, you can configure rules that control when Autotask tickets are created.
-
Select Do not send PSA ticket if no password is found to prevent ticket creation for compromises that do not include a password. This reduces ticket noise and ensures only that actionable incidents generate Autotask tickets.
-
The Enable processing of IP address–related compromises to PSA integration checkbox allows IP address–related compromises to be sent to Autotask.
Default behavior:
-
Both ticket conditions are disabled by default. In this state, only email and domain compromises (with or without passwords) are sent to Autotask; IP address-related compromises are excluded.
When enabled:
-
IP address–related compromises are also created as Autotask tickets.
The Autotask Company Mapping section allows you to align Autotask company names with Dark Web ID organization names so that compromises are sent to the correct company in Autotask.
This section displays three columns that help identify and resolve naming mismatches between the two systems:
-
Autotask Account Names: Lists companies retrieved from Autotask.
-
Matched Organizations: Shows companies that already have a matching Dark Web ID organization name. No action is required for matched entries.
-
Non‑Matching Organizations: Displays Autotask companies that do not currently match any Dark Web ID organization.
Resolving non‑matching organizations
For companies listed under Non‑Matching Organizations, click Edit to modify either the Autotask company name or the Dark Web ID organization name so they exactly match. Once the names align, the company moves into the Matched Organizations column.
NOTE Tickets are created only for matched companies. If a company is unmapped, no tickets are created—even though it may appear in the Total Autotask Accounts count, which includes all companies retrieved from Autotask regardless of match status. Each Dark Web ID SMB organization can be associated with only one Autotask integration.
The Field Mappings section defines how Dark Web ID compromise data is written into specific Autotask service ticket fields when a PSA ticket is created. In this section, you map Autotask ticket fields to Dark Web ID tokens, which dynamically populate ticket content with relevant compromise details.
Adding a field mapping
Click + Add Field Mapping to create a new mapping. Each mapping includes:
-
Autotask Field: The Autotask service ticket field to populate
-
Content: Enter static text, Dark Web ID tokens, or a combination of both. Tokens are replaced with real compromise data at ticket creation time.
NOTE Content values may be trimmed to the maximum character length supported by the selected Autotask field.
Required field mappings
Several required field mappings are provided by default to support Autotask ticket creation. These mappings correspond to a subset of Autotask service ticket fields and must remain configured for the integration to function correctly.
The following required fields appear in the mapping interface:
-
Ticket Title (string): Text written to the Autotask ticket title
-
Organization (integer): Autotask organization associated with the ticket
-
Ticket End Date (datetime): Calculated using a Days value
-
Ticket Status (integer): Initial Autotask ticket status
-
Ticket Priority (integer): Initial ticket priority
-
Destination: Additional routing or classification (optional content)
IMPORTANT Incorrect or missing mappings can cause ticket creation to fail. Changes take effect immediately after you save them.
Available Autotask fields
In addition to the required fields listed above, Dark Web ID supports mapping to the following Autotask service ticket fields.
Availability depends on the Autotask ticket type and your Autotask configuration.
-
Ticket Title (string)
-
Ticket Description (string)
-
Ticket Status (integer)
-
Ticket Priority (integer)
-
Ticket Category (integer)
-
Ticket Queue Name / Ticket Department Name (integer)
-
Ticket Type (integer)
-
Ticket Source (integer)
-
Ticket Contact (integer)
-
Organization / Account (integer)
-
Ticket End Date (DateTime)
-
Ticket Estimated Hours (double)
-
Resolution Plan Date Time (DateTime)
-
Resolved Due Date Time (DateTime)
-
External Ticket ID (string)
-
Purchase Order Number (string)
NOTE Not all fields are available for every Autotask ticket type. Field availability and validation rules are enforced by Autotask.
Using tokens
The Token table on the right side of the page lists all available Dark Web ID tokens and their descriptions. These tokens can be inserted into the Content field for any supported Autotask field.
Tokens appear in square brackets (for example, [uuid]) and are replaced with live compromise data when the Autotask ticket is generated.
Example: Token usage in Content
The mapping UI shows Content values that include multiple tokens, such as:
[uuid]
[record_type]
[search_value]
[password]
When a ticket is created:
-
[uuid] resolves to the unique compromise ID
-
[record_type] identifies the compromise type (Email, Domain, or IP)
-
[search_value] contains the affected email address, domain, or IP
-
[password] is included when password data is available
NOTE You can add static labels (for example, Record type: or Affected value:) to make the ticket description easier to read.
Where available tokens come from
The Token and Token Description columns on the right side of the page show all available Dark Web ID tokens and explain what each one represents. You can reference this list at any time while building field mappings.
-
[uuid] Dark Web ID’s unique identifier for the Compromise. (text)
-
[password] The password hit associated with the Compromise [This does not include IP address related compromises]. (text (255))
-
[obscured_password] The password hit associated with the Compromise obscured with asterisks after the first four characters. (text (255))
-
[record_type] The type of record monitored: Email, Domain, or IP. (text (255))
-
[source] The record source as reported in Dark Web ID. (text (255))
-
[origin] The record website as reported by Dark Web ID. (text (255))
-
[organization_name] The name of the Organization to which the Compromise belongs. (text (255))
-
[compromise] The record compromise as reported in Dark Web ID. (text (255))
-
[password_criteria] An indication of whether the Compromised Password meets the Organization’s Password Criteria: ‘N/A’ ‘Matches’ ‘Doesn’t Match‘. (text (255))
-
[search_value] The Email or IP Address found by Dark Web ID. (text (255))
-
[date_added] The date on which the Compromise was added to Dark Web ID. (date)
-
[date_found] The date on which the Compromise was found. (date)
-
[pii] The Personal Identifiable Information found. (text (255))
Character limits
Each Autotask field enforces a maximum character limit. After token substitution, content is automatically trimmed if it exceeds the field’s allowed length.
Key takeaways
-
Required Autotask field mappings must remain configured
-
Content can include static text, tokens, or both
-
Tokens are resolved at ticket creation time
-
The token table is the authoritative reference for available values
To save and test the integration, click Save or Save And Submit A Test Compromise in the lower-right corner of the page to validate your configuration.
A test ticket will be created in Autotask using sample data. If the test is successful, you will see a confirmation message.
If you encounter any errors, please review the field mappings and permissions. For further assistance, contact support@idagent.com.
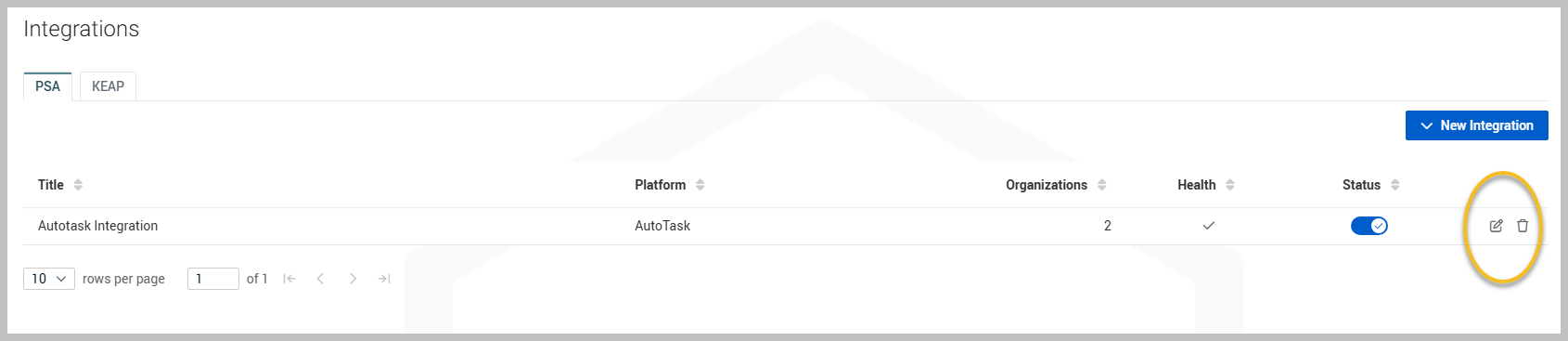
Each integration displays a health status:
-
Healthy (✓): This indicates that your most recent integration request was successful.
-
Unhealthy (✗): This indicates that your most recent integration request was unsuccessful or encountered an error. This status will remain until a successful integration request is completed.
NOTE Integration is marked unhealthy after the fifth unsuccessful consecutive attempt. The errors will be shown on the Edit Integration screen.
You can edit the integration using the edit icon, and the delete icon will completely delete your integration.
-
Integrations are disabled by default. You can enable your integration using the toggle button.
-
After clicking the toggle, you will be prompted to enable the integration. Click Enable to activate the Autotask integration.
-
The status bar turns blue when active.
-
Once enabled, all new compromises imported into Dark Web ID will attempt to create service tickets in Autotask. You can enable or disable integrations at any time.
Enabling the integration globally is not sufficient—you must also enable it per SMB.
There are two ways to edit an organization and manage its integrations:
-
From the Organizations page
-
From the Integrations page
Both methods are supported.
Enable an integration from the Organizations page
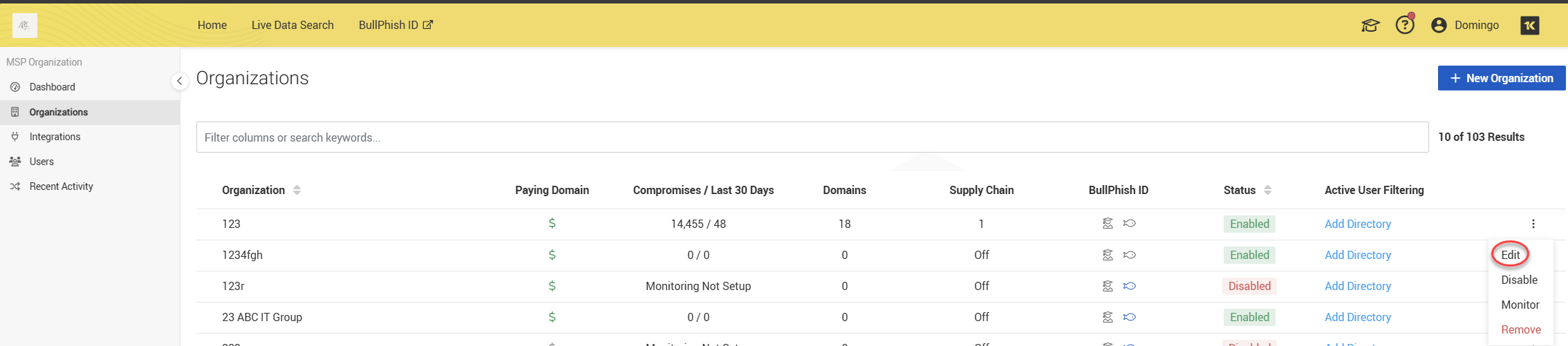
1. Open the Organizations page from the side navigation menu.
2. Open the organization’s actions menu (three dots) and select Edit.
3. Scroll to the Associated Integrations section.
4. Select the Autotask Integration (or your given integration title) checkbox and click Save.
Enable an integration from the Integrations page
1. Open the Integrations page from the side navigation menu.
2. Locate the Autotask integration and click the pencil icon to edit it.
3. Click Edit to open the SMB Edit page of the organization you wish to modify.
4. Scroll down to view the Associated Integrations section.
5. Select the Autotask Integration (or your given integration title) checkbox and click Save.
IMPORTANT If an organization is disabled, monitoring will continue, and the integration will remain active. While PSA notifications will still be generated, email notifications will not be sent to this organization. If you need to prevent PSA tickets from being created, you can do so by clearing the checkbox for the Autotask Integration (or the specific integration title) in the Associated Integrations section.
You can view the number of organizations linked to Autotask on the Integrations page.
.png)